Pricing is one of the most critical decisions you’ll make in your business. A well-thought-out pricing strategy can increase profits, strengthen your brand, and drive long-term customer loyalty. This guide dives deep into proven pricing theories and practical applications to help you price your product for maximum profitability.
1. Understand Your Costs
Before pricing any product, you must understand the costs involved. These include:
- Fixed Costs: Rent, salaries, software subscriptions.
- Variable Costs: Materials, packaging, shipping.
- Semi-variable Costs: Utilities, part-time labor.
Your price must cover all these costs and generate profit.
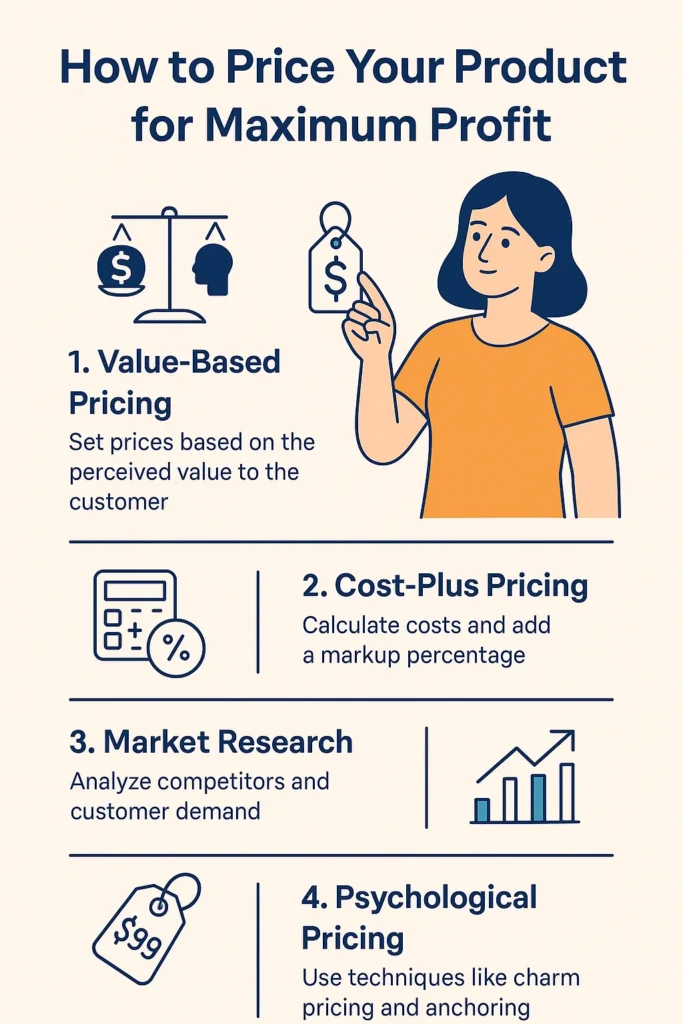
Use the formula: Price = Cost + Desired Profit Margin.
2. Choose a Pricing Model
Different pricing strategies serve different business goals. Here are the main models:
- Cost-Plus Pricing: Add a standard markup to your cost. Simple but ignores market demand.
- Value-Based Pricing: Set prices based on the perceived value to the customer. Ideal for premium products.
- Penetration Pricing: Set a low price to enter the market quickly, then increase over time.
- Skimming Pricing: Launch high to capture early adopters, then lower prices to attract broader segments.
3. Conduct Market Research
Understanding your competitors’ pricing helps you position your product effectively. Tools like SEMrush, Google Trends, and competitor websites can provide valuable insights.
Ask: Where do you want your product to sit in the market — premium, mid-tier, or budget?
4. Apply Psychological Pricing
People don’t always behave rationally when it comes to prices. Use these tactics:
- Charm Pricing: $9.99 feels cheaper than $10.00.
- Price Anchoring: Show a higher original price next to a discounted one.
- Tiered Pricing: Offer three options (basic, standard, premium) to guide customer choices.
5. Test and Iterate
Your first price won’t be your last. Use A/B testing, monitor conversion rates, and analyze customer feedback.
Over time, tweak your pricing to better align with your business goals and customer behavior.
6. Bonus: SaaS Pricing Tiers Example
For SaaS and digital product businesses, use a 3-tier model:
- Basic: Limited features for entry-level users.
- Standard: Most popular with balanced features.
- Premium: Full access with concierge support.
This appeals to different customer segments and maximizes value extraction.
Conclusion
Pricing is both an art and a science. With a solid understanding of your costs, value proposition, customer psychology, and competition, you can craft a pricing strategy that drives revenue and growth.
Ready to build a pricing model tailored to your business? Use tools like ProfitWell, HubSpot’s Pricing Calculator, or try out value-based pricing calculators online.